

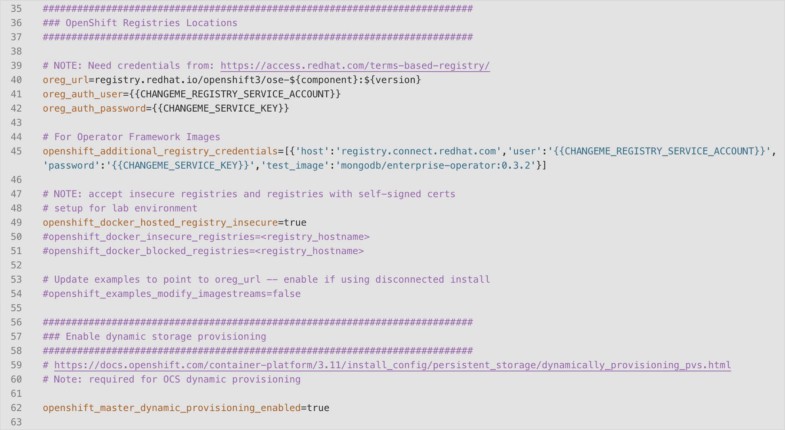
I will not delve into these details here. Osm_etcd_image: satellite.mydomain:5000/MyOrg-ocp311-rhel7_etcd:3.2.22 Post-installation configurationĭepending on which applications you want to use in your OpenShift cluster, you may want to modify your image streams accordingly. Oreg_url: satellite.mydomain:5000/MyOrg-ocp311-openshift3_ose-$ will not work for etcd therefore, you must specify the exact etcd docker image URL: I will provide further instructions in the next section.ĭocker pull satellite.mydomain:5000/MyOrg-ocp311-openshift3_ose-pod:v3.11.69 Red Hat OpenShift Ansible inventory modificationsįor the installer to be able to use the Docker registry on Red Hat Satellite, restructure oreg_url as following: If you do not tell the Red Hat OpenShift installer about this change, the installation will fail. This means the URL of a Docker image will change from: The Red Hat Satellite server implements a Docker registry slightly differently from traditional Docker registries. Hammer product synchronize -name "ocp311" -organization "MyOrg"Įnsure you add the product to the content view that your OpenShift will be registered to access. Once you have created all the repositories, you can either synchronize using the GUI or via the command line: Hammer repository create -name "openshift3/ose-node" -content-type "docker" -url "" -docker-upstream-name "openshift3/ose-node" -product "ocp311" -organization "MyOrg"
For example, to create a product for openshift3/ose-node, use the following command: This is what makes Red Hat Satellite behave slightly differently from other registries, as Red Hat Satellite will synchronize this image with the upstream server (), including all its versions. Then, you will need to create a repository for each image. Hammer product create -name "ocp311" -organization "MyOrg" On the Red Hat Satellite server, create a product within the organization that your Red Hat OpenShift nodes will be registered to Openshift_pkg_version: -3.11.69 Red Hat Satellite settings This should be reflected in your inventory as follows:
#Openshift ansible docker insecure registry install#
This work is based on the following references: I also discuss adjustments that may be required post install. In this article, I will discuss the prerequisites and requirements for the successful implementation of Red Hat OpenShift 3.11 disconnected installation using Red Hat Satellite as the local Docker registry, which I have been able to do with the support of my colleagues.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
